In this article, we are going to discuss about generations of computer.
- First Generation Computers
- Second Generation Computers
- Third Generation Computers
- Fourth Generation Computers
- Fifth Generation Computers
Computers have evolved through different generations. Let us explore this journey in detail.
What is Generation?
Generation refers to the state Of improvement in product development process. Similarly, we can say generation of computer refers to the state of improvement in computer technology.
Accordingly, the computers are classified into five generations. Let’s study about each generation individually.
1. First Generation Computers (1946-1958)
- The first generation computers were made from the year 1946 with ENIAC (Electronic Computer and UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) that were developed by Presper Eckert and John Mauchly.
- First generation computers used vacuum tubes.
- Language used in first generation computers was machine language.
- They were very large in size and produced a large amount of heat. They had to be cooled down by air conditioners.
- The operating speed was very slow. They were not reliable.
- The other first generation computers were Mark I, EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer), EdSAC, (Electronic Delayed Storage Automatic Computer), INM 650, Mark II.
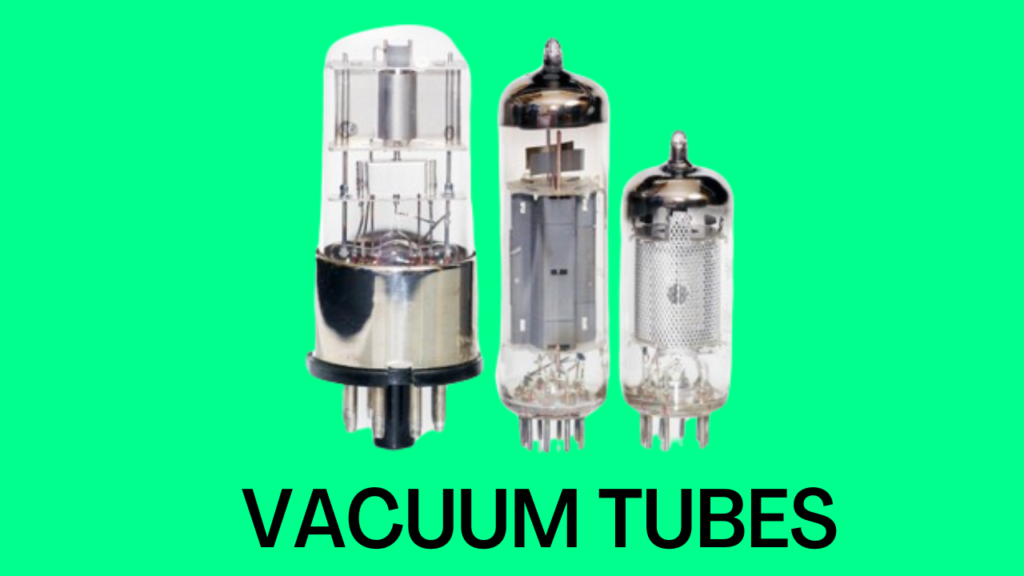

Features of First Generation Computers
| Electronic component used | Vacuum tubes |
| Size | Very huge (as big as the size of the room) |
| Operating speed | Very slow |
| Cost | Very expensive |
Limitations of First Generation computers
- Produced lot of heat
- Programming capacity was very low
- Not reliable
- Used machine language only
Due to the above limitations and drawbacks, more advanced computers developed, which were the second generation computers.
It’s a fact!
ENIAC was the first electronic computer. The total cost of ENIAC , which weighed over 25 tons and took up approximately 680 square feet, was $500,000. That’s about $6 million in today’s money.
2. Second Generation Computers (1959 – 1964)
- The second generation computers were introduced in the late 1950s which replaced vacuum tubes with transistors.
- The language used in the second generation computers was assembly language.
- The second generation computers also produced a large amount of heat and they too had to be cooled down by air conditioners.
- They were smaller, faster and more efficient than the first generation computers.
- The operating speed was comparatively high.
- Examples of second generation computers were IBM 140, Mark III, LEO etc.
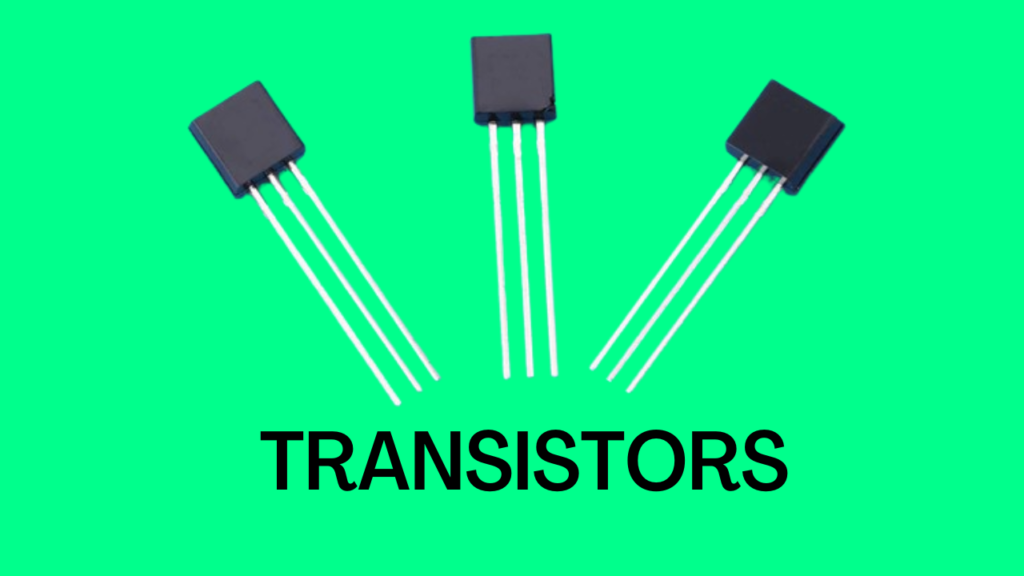
Features of Second Generation Computers (1959-1964)
| Electronic component used | Transistors |
| Size | Became smaller than first generation computers |
| Operating speed | Became higher |
| Cost | Became low |
| Language Used | Assembly Language |
Limitations of Second Generation Computers
- Produced heat
- Speed was still low
- Memory was less
Due to the above limitations and drawbacks, the more advanced computers developed, which were the third generation computers.
Did You Know?
Second generation computers were the first computers that stored instructions in their memory.
3. Third Generation Computers (1965-1972)
- The third generation computers, introduced in 1965, used the first Integrated Circuits (ICs) and the first operating system.
- Due to the use of ICs, the size of the computer became very small.
- Transistors were miniaturized and placed on silicon chips called semiconductors.
- High level languages like FORTRAN and COBOL were used.
- The processing speed was comparatively high.
- It used less power and radiated less heat.
- Examples of third generation computers are ICL, CDC, IBM 360, ICL 1900, etc.
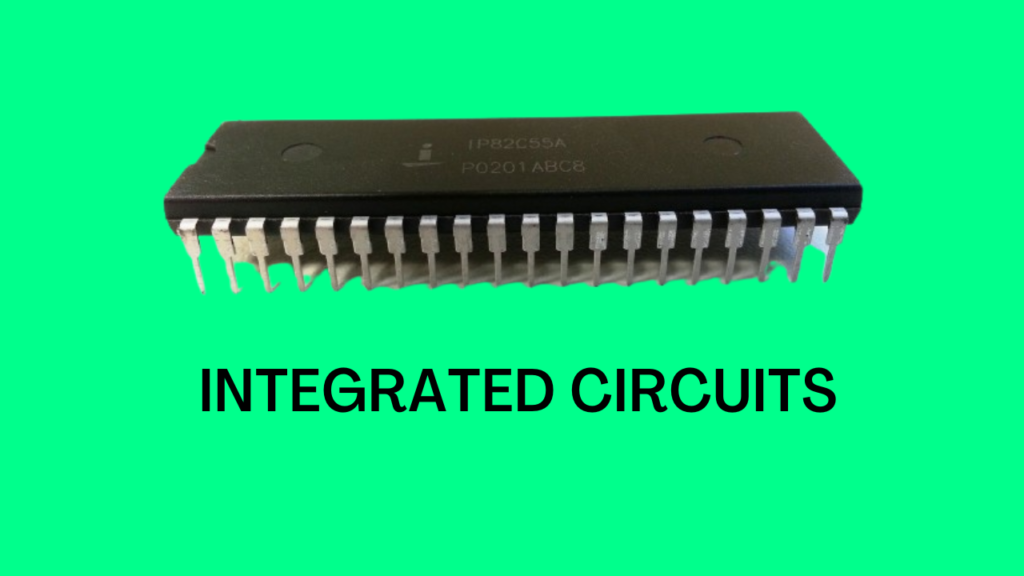
Features of Third Generation Computers
| Electronic component used | Integrated Circuits |
| Size | Became much smaller |
| Operating speed | Faster |
| Cost | Became cheaper than their predecessors |
| Language Used | High Level Language |
Did You Know?
- The integrated circuits were also called chips.
- In third generation computers, instead of punched cards and printouts, users, interacted through keyboards and monitors.
4. Fourth Generation Computers (1972-1984)
- The fourth generation computers, introduced in 1972, brought us computers made entirely of chips.
- The size of the computer became too small as thousand of integrated circuits were built onto a single silicon chip.
- Fourth generation computers could fit on a small desk or in the palm of the hand.
- The fourth generation computers became more powerful and they could be linked together to form a network, which led to the development of internet.
- They are completely reliable.
- Today’s fourth generation computers are still getting smaller and more powerful.
- Examples of fourth generation computers are Intel 4004, Apple-II, IBM 370, etc.

Features of fourth Generation Computers
| Electronic component used | Microprocessor |
| Size | Became much smaller than ever |
| Operating speed | Became very fast |
| Cost | Became cheaper than their predecessors |
| Reliability | Completely reliable |
Did You Know?
The first IC was developed in 1950’s by Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce.
5. Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond)
- Computers today have some attributes of fifth generation computers.
- Fifth generation computers use artificial intelligence which means computers have been programmed to take decisions.
- The goal of fifth generation computing is to develop devices that respond to natural language and are capable of learning and self organization.
- A robot is a good example – it is a mechanical, virtual, artificial agent.

Artificial Intelligence
Features of Fifth Generation Computers
| Electronic component used | Artificial Intelligence |
| Size | Very Small |
| Operating speed | Extremely High |
| Memory | Very Fast |
| Features | 1st Generation (1946-1958) | 2nd Generation (1959-1964) | 3rd Generation (1965-1972) | 4th Generation (1972-1984) | 5th Generation (Present & Beyond) |
| Processor | Vacuum Tubes | Transistors | Integrated Circuits (ICs) | Microprocessor | Artificial Intelligence |
| Input | Punched Cards | Punched Cards | Keyboard | Keyboard, Mouse | Automatic System |
| Output | Printer | Printer | Monitor, Printer | Monitor, Printer | Auto Intelligence |
| Memory | Magnetic Drums | Magnetic Drums | Magnetic Disks | Magnetic Disks | Auto Decisions |
| Size | Very Huge | Smaller than 1st Generation | Smaller than 2nd Generation | Smaller than 3rd Generation | Very much reduced |
| Speed | Slow | Fast | Faster | Faster | Very Fast |
| Cost | Very high | Less | Less | Less | Very less |
| Examples | ENIAC and UNIVAC | IBM 704 | IBM 360, IBM 195 | Intel Pentium 4 | ASIMO |
Time for a Recall
- Generation of computer refers to the improvement in the development of computer technology.
- The computer generation are classified into five generations.
- The first generation computers used vacuum tubes.
- In second generation, the vacuum tubes are were replaced by transistors.
- Integrated circuits were the hallmark in the development of third generation computers.
- The fourth generation computers use a microprocessors.
- The fifth generation computing devices are based on Artificial Intelligence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A. Answer the following questions:
1. Very short answer questions:
Q.1 How many generations of computer are there?
Ans.1 There are five generations of computer.
Q.2 Name the electronic component and language used in:
| Generations | Electronic Components | Language |
| 1st Generation | ||
| 2nd Generation | ||
| 3rd Generation | ||
| 4th Generation | ||
| 5th Generation |
| Generations | Electronic Components | Language |
| 1st Generation | Vacuum Tubes | Machine Language |
| 2nd Generation | Transistors | Assembly Language |
| 3rd Generation | Integrated Circuits | High Level Language |
| 4th Generation | Microprocessors | RDBMS |
| 5th Generation | Artificial Intelligence | Natural Language |
Q.3 Give two examples of second generation computers.
Ans.3 IBM 704 and MARK III are the two examples of second generation computers.
Q.4 Name two computers of first generation.
Ans.4 ENIAC and UNIVAC are the two computers of first generation.
Q.5 Name the developers of the first integrated circuit.
Ans.5 Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce
2. Short answer questions:
Q.1 What do you mean by generation of computers?
Ans.1 Generation of computer refers to the improvement in the development of computer technology.
Q.2 What is the difference between first generation computers and second generation computers?
Ans.2 There are following difference between first generation computers and second generation computers.
| First Generation Computers | Second Generation Computers |
| The first generation computers were introduced in the year 1946. | The second generation computers were introduced in the year 1950. |
| First Generation Computers used vacuum tubes. | Second generation computers used transistors. |
| The Language used in first generation computers was machine language. | The Language used in second generation computers was assembly language. |
| First Generation Computers were very large in size. | Second generation computers were small in size as compared to the first generation. |
| The operating speed was very slow. | The operating speed was comparatively high. |
| The cost of first generation computers were very expensive. | The cost of second generation computers were low as compared to the first generation. |
| Examples of first generation computers were ENIAC, UNIVAC, MARK I, EDVAC, EDSAC, INM650, MARK II. | Examples of second generation computers were IBM 140, MARK III, LEO, etc. |
Q.3 What is a microprocessor?
Ans.3 A small unit of computer that contains all the functions of the central processing unit. It operates on number and symbols represented in the binary number system.
3. Fill in the blanks:
- The first generation of computers was started in __________.
- ______________ and _______________ were the first generation computers.
- The integrated circuits are also called ____________.
- Transistors were placed on _____________________ called semiconductors.
- The third generation of computers used ______________________.
Ans.3 (1) 1946 (2) ENIAC and UNIVAC (3) Chips (4) Silicon Chips
(5) Integrated Circuits
Know More: https://digitalcomputereducation.com/introduction-to-python-programming/
Read More: https://youtu.be/Hjn4C_dgNqI

